Tissue Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit (Proteinase K & Carrier RNA included)
Tissue Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit is designed for rapid and efficient purification of viral nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) from infected tissue. The purification is based on the usage of denaturing agents to provide efficient tissue lysis as well as viral lysis, denaturation of proteins and subsequent release of DNA or RNA. Special buffers provided in the kit are optimized to enhance the binding of DNA or RNA onto a speciallytreated glass filter membrane for efficient recovery of highly pure DNA or RNA. The extracted DNA or RNA can be used for various applications, including PCR, RFPL, and other molecular testings.
Tissue Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit is designed for rapid and efficient purification of viral nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) from infected tissue. The purification is based on the usage of denaturing agents to provide efficient tissue lysis as well as viral lysis, denaturation of proteins and subsequent release of DNA or RNA
Final price excl. shipping costs3
- verfügbar / avaílable
- 1 - 3 days for delivery / 1 - 3 Tage Lieferzeit1
Description:
The Tissue viral RNA/DNA Extraction Kit is designed for rapid and efficient purification of genomic DNA from various tissue
samples such as lungs etc. or swabs and nasopharyngeal swab salivia, sputum. The purification is based on the usage of denaturing agents to provide lysis of tissue cells, denaturation of proteins
and subsequently release of viral RNA/DNA. Special buffers provided in the kit are optimized to enhance the binding of DNA onto a specially-treated glass filter membrane for efficient
recovery of highly pure genomic RNA/DNA.
Features Tissue Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit:
- Mini-column spin technology
- No organic-based extraction required
- Highly pure genomic DNA ready to use for routine molecular biology applications such as restriction enzyme digestion, PCR, -
Southern blotting, DNA fingerprinting, etc.
The expected yield is up to 3ug, depends on elution volume and sample types (raw tissue or cooked tissue or tissue organ).
Application:
For high quality tissue RNA/DNA isolation.
As for: swabs and nasopharyngeal swab samples
1. Scrape the swabs firmly against the samples 6-7 times.
2. Cut the end of the swab stick containing the sample and place it into a 2ml microcentrifuge tube.
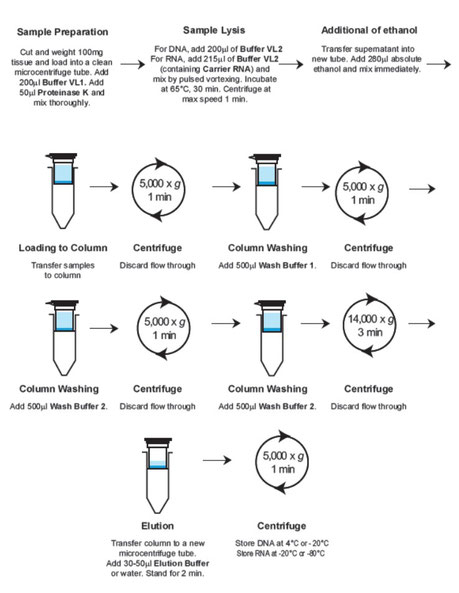
3. Add 550ul PBS, 50ul Proteinase K and 200ul Buffer VL1 to the sample. Mix thoroughly by vortexing.
4. For extraction of viral RNA, add 215ul of Buffer VL2 containing Carrier RNA. Mix homogeneously by pulsed-vortexing. Incubate at 65C for 30 min. Centrifuge at maximum speed for 1 min. Transfer supernatant into a new microcentrifuge tube. Continue step 2 (Addition of ethanol) stated at GF-TRD manual.
As for: salivia, sputum samples
1. Collect 1.5ml saliva and sputum into a clean 15ml centrifuge tube containing 6ml PBS. Mix thoroughly by vortexing.
2. Centrifuge at 2000 xg for 5 min. Discard the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 180ul PBS.
3. Transfer the samples into a clean 1.5ml microcentrifuge tube.
4. Add 50ul Proteinase K and 200ul Buffer VL1 to the sample. Mix thoroughly by vortexing.
5. For extraction of viral RNA, add 215ul of Buffer VL2 containing Carrier RNA. Mix homogeneously by pulsed-vortexing. Incubate at 65C for 30 min. Centrifuge at maximum speed for 1 min. Transfer supernatant into a new microcentrifuge tube. Continue step 2 (Addition of ethanol) stated at GF-TRD manual.
Note:
Tissue Viral Nucleic Acid samples vary in the number of cells depending on age, type of tissue
and origin. When processing samples, do not use more than the recommended starting material as excessive number of cells will overload the column. This would result in reduced yield and purity.
We recommend weighing the tissue samples before starting to ensure optimum yield and purity is obtained. Liver and spleen are very high in protein and RNA content. Thus, when isolating genomic
DNA from these sources, use only up to 15mg of the sample.
Comparison Tissue Viral Nucleic Purification Kit
DNA/RNA purification: Selection sheet
Sample request Tissue Viral Nucleic Extraction kit
Dear customer, GeneON likes to send samples to convince the valued customer about the quality. Please understand that the shipping costs may be very high to some destinations. That is the reason why we cannot assure to fulfil all sample requests. Sorry for that, please understand. You may also set an inquiry/order directly by e-mail .
Related products
Overview Extraction Kits
Bacterial DNA Mini-Prep Purification
Tissue DNA Mini-Prep Purification
Plant DNA Mini-Prep Purification
Blood DNA Mini-Prep Purification
Food DNA Mini-Prep Purification
Plasmid DNA Mini-Prep Purification
Ambi Gel/PCR DNA Mini-Prep Purification
PCR Clean-up Mini-Prep Purification
Gel Extraction Mini-Prep Purification
Soil sample DNA Mini-Prep Extraction
Forensic DNA Mini-Prep Extraction
Total RNA Mini-Prep Extraction
Deutsche Beschreibung
Tissue Tissue Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit: Manual
MSDS Tissue RNA Extraction Mini-Prep Kit
References
Alabsi, A.M., et al. (2016) Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
Induction via Modulation Mitochondrial Integrity by Bcl-2 Family Members and Caspace Dependence in Dracaena cinnabari-Treated H400 Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BioMed
Research International.
Chontananarth, T. (2016) Multiplex PCR assay for
discrimination of Centrocestus caninus and Stellantchasmus falcatus. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine.
Chuah,L.O., He, X.B., Effarizah, M.E., Syahariza, Z.A., Shamila-Syuhada, A.K., Rusul, G. (2016) Mislabelling of beef and poultry products sold in Malaysia. Food Control. 62.
Pp157-164
Abdo el Motalab, Y.S., & Ahmed, A.B. (2014) Isolation and
Identification of Camelpox Virus in Eastern Sudan SUST Journal of Agricultural and Veterinary Sciences (SJAYS). 15(2), p. 73-81.
Chontananarth, T., Wongsawad, C., Chomdej, S., Krailas, D., Chai, J.Y. (2014) Molecular phylogeny of trematodes In Family Heterophyidae based on mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (mCO I). Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical
Medicine. Pp..446-450.
Noikong, W., Wongsawad, C. (2014) ) Epidemiology and
molecular genotyping of echinostome metacercariae in Filopaludina snails in Lamphun Province, Thailand. Asian Pacific journal of tropical Medicine. 7(1). Pp.26-29.
Sade, A., & Biun, H. (2009)Detection of Pig Residue in Fish Feedstuffs and Fish
Stomach Content Using Polymerase Chain Reaction for Halal Certification Proceedings of the 5th National Fisheries Symposium 2008: Kuala Terengganu (Malaysia), 2008: 143-148





