Total RNA Aufreinigungs-/Extraktionskit (Mini prep Kit) mit "spin column" Technik
Isolierung hochwertiger Gesamt-RNA aus tierischen oder menschlichen Zellen und Geweben
Total RNA Isolation: Schnell und effizient! Extraktion von Gesamt-RNA aus Gewebe oder kultivierten Zellen
The Total RNA Extraction Kit is designed for the isolation of total RNA (longer than 200 bases) from a variety of sources such as animal tissues, bacteria cells and cell cultures, ethanol not included
Final price excl. shipping costs3
- verfügbar / avaílable
- 1 - 3 days for delivery / 1 - 3 Tage Lieferzeit1
Beschreibung:
Das GF-1 Total RNA Isolierungskit wird verwendet für die einfache und schnelle Isolierung qualitativ hochwertiger Gesamt-RNA aus tierischen oder menschlichen Zellen
und Geweben.
Die Proben werden unter denaturierenden Bedingungen mit einem speziellen Puffer lysiert und danach auf das Column gegeben. Dort bindet die RNA selektiv und reversibel an die spezielle Glasfilter-Membran.
Spezielle im Kit enthaltene Puffer optimieren die Bindung der RNA auf eine spezielle Glasfilter-Membran zur effizienten Gewinnung hochreiner RNA.
Features:
- Gewinnung von bis zu 3 µg Gesamt-RNA
- Mini column Spin-Technologie
- Keine organisch-basierte Extraktion nötig
- Die hochreine Gesamt-RNA kann für alle Arten von Folgeexperimenten
in der Molekularbiologie, wie RT-PCR, Northern Blotting, polyA-RNA
(mRNA) Reinigung und in vitro-Translation weiterverwendet werden.
Anwendung: Zur Reinigung von Gesamt-RNA aus Zell-basierten Proben.
Kit Bestandteile:
- RNA binding columns
- Homogenization columns
- Collection tubes
- Puffer TR*
- Inhibitor Removal Puffer*
- Waschpuffer*
- DNase I*
- Verdaupuffer
- Verdau Verstärker
- RNase-freies Wasser
- Proteinase K*
- Handbuch
* Bitte beachten Sie Verdünnung von Lösungen und Lagerung und Stabilität vor der Verwendung dieses Kits.
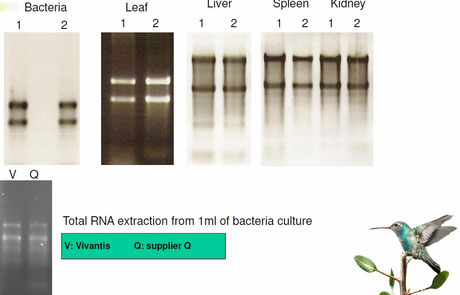
Vergleich mit anderen Total RNA Aufreinigungskits
Neu, nun auch als 96-Platte verfügbar
5x96: Total RNA Extraction Kit is designed for rapid and high-throughput purification of total RNA from bacterial cultures, viruses, plant and animal tissues, up to 96 samples simultaneously
Final price, free shipping to selected countries3
Free shipping to the following countries: Germany
- verfügbar / avaílable
- 1 - 3 Months for delivery / 1 - 3 Monate Lieferzeit1

DNA/RNA purification: Selection sheet
RNA-Aufreinigung aus Gewebe: Musterbestellung
Wir bitten um Verständnis, dass kostenlose und unverbindliche Muster nur innerhalb von Deutschland versendet werden. Um Ihren Auftrag schnell zu bearbeiten, bitten wir Sie die Lieferadresse vollständig anzugeben. Für UPS Express benötigen wir auch Ihre Telefonnummer. Alternativ können Sie auch gerne eine Anfrage/Bestellung per E-mail senden.
Related products
Taqs:
DNA, column, rna isolation prep, lysis pcr, spin
MSDS RNA Extraction Mini-Prep Kit

References
Liu, T., Liu, F., Wang, C., Wang, Z., Li,Y. (2017) The
boosted biomass and lipid accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris by supplementation of synthetic phytohormone analogs. Bioresource Technology. 232. Pp..44-52
Waziri, P.M., Abdullah, R., Yeap, S.W., Omar, A.R., Abdul, A.B., Kassim, N.K., Malami, I., Karunakaran,T., Imam, M.U. 2016. Clausenidin from Clausena excavata induces apoptosis in hepG2 cells via the mitochondrial
pathway. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 194 pp.549-558.
Abu-Elsaad,N.M., Serrya, M.S., El-Karef, A.M., Ibrahim, T.M.
(2016).
Kaplan, S. et al. (2016) The Potential of Microarray Databases
to Identify Tissue Specific Genes Kafkas Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi,22(1), p. 29-35.
Loosse, C., Pawlas, M., Bukhari, H.S.S., Maghnouj, A., Hahn, S., Marcus, K., Müller, T. (2016) )Nuclear spheres modulate the expression of BEST1 and GADD45G. Cellular
Signalling. 28. Pp.100-109.
Ng, S.L., Harikkrishna, J.A., Bakar,F.A., Yeo, C.C., Cha, T.S. (2016) Heterologous expression of the Streptococcus pneumoniae yoeB and pezT toxin genes is lethal in Chlorella vulgaris. Algal Research. 19 pp.21-29
Saregah, N., et al (2016) Effects of Phenolic-rich Extracts if
Clinacanthus nutans on High Fat and High Cholesterol Diet-induced Insulin Resistance BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine16(88), p.1-11.
Moghadam, F.H., et al. (2015) Differentiation of Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into
Adipocytes and Cardiomyocytes after Treatment with Platelet Lysate. International Journal of Hematology-Oncology and Stem Cell Research. 10(1), p. 21-29.
Shalabi,M.,Khilo, Kh., Zakaria, M.M., Elsebaei, M.G., Abdo, W., Awadin, W. (2015) Anticancer activity of Aloe vera and Calligonum comosum extracts separetely on
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine. 5(5) pp.375-381.
Hassanin, A., et al. (2014) Heparin Modulation on Hepatic
Nitric Oxide Synthase in Experimental Steatohepatitis. Experimental and Theapeutic Medicine. 8, p. 1551-1558.










